THE BEST IN TECH FOR ATSC. 3.0
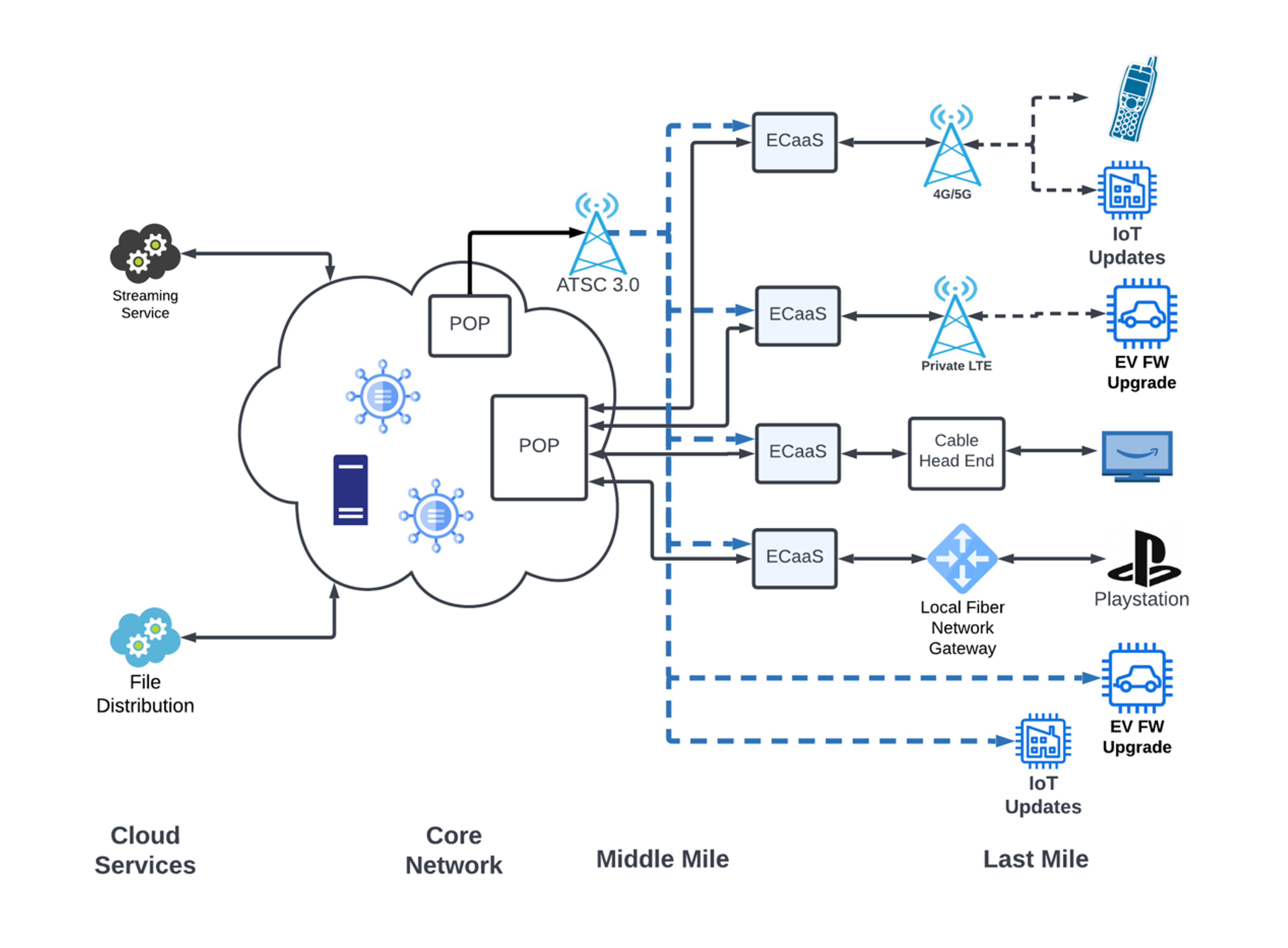
A smarter pathway to the edge.
ATSC 3.0 Spectrum
Data applications using the PEAK3 network and its underlying ATSC 3.0 platform will have several advantages over a traditional cellular network for many applications and services:
Do you think we are a good fit yet? Want to learn more?
ATSC 1.0
- MPEG-2 transport stream provides service flexibility for multicasting.
- Broadcasting isn’t part of the internet and it’s massive global investment.
ATSC 3.0
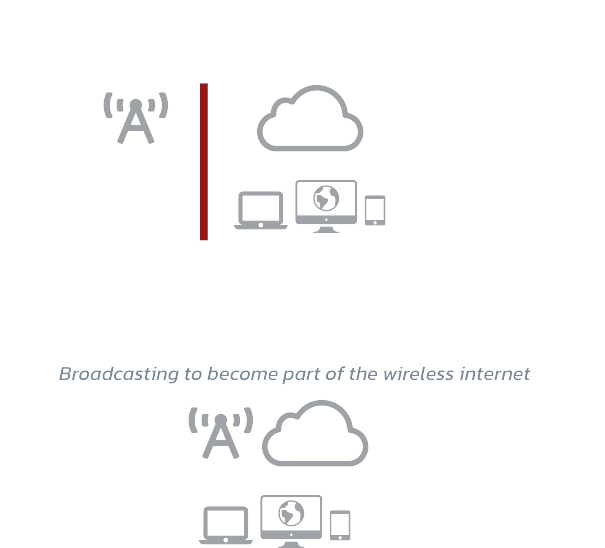
- Internet protocol based – enable broadcasting to become part of the wireless internet
- Encryption conditional access/DRM enables monetization
- File delivery enables VOD and Dynamic Ad Insertion

The IP-based ATSC 3.0 standard changes the playing field.
ATTSC 3.0 ushers in a large-scale advantage for broadcasting technology that brings together the capabilities of over-the-air (OTA) broadcasting, the internet, and a host of additional use cases that provide the opportunity for PEAK3 to partner with broadcasters and generate revenue streams.
Slicing
Slicing Segments of a television station’s edge server capacity can be configured to transmit data to different ATSC 3.0-capable devices, providing the right services for each use case and enabling connected intelligence opportunities such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). Likewise, network spectrum can be configured to offer specific bandwidth slices for different purposes.
Edge Orchestration
Edge orchestration makes it possible to dynamically and automatically allocate and release spectrum and broadcast system resources in a virtualized, cloud-based environment.
Leased Spectrum Facilitation
Leased spectrum facilitation Monetize excess broadcasting spectrum capacity by leasing these bits to other entities that will use them to deliver their own content, data, or even internet services.
Interactivity and audience measurement
Interactivity and audience measurement In ATSC3.0, user equipment is connected via the IP backbone. This provides additional flexibility to target regions with specialized services, for example with focused advertising by subregion, thereby driving additional revenue.
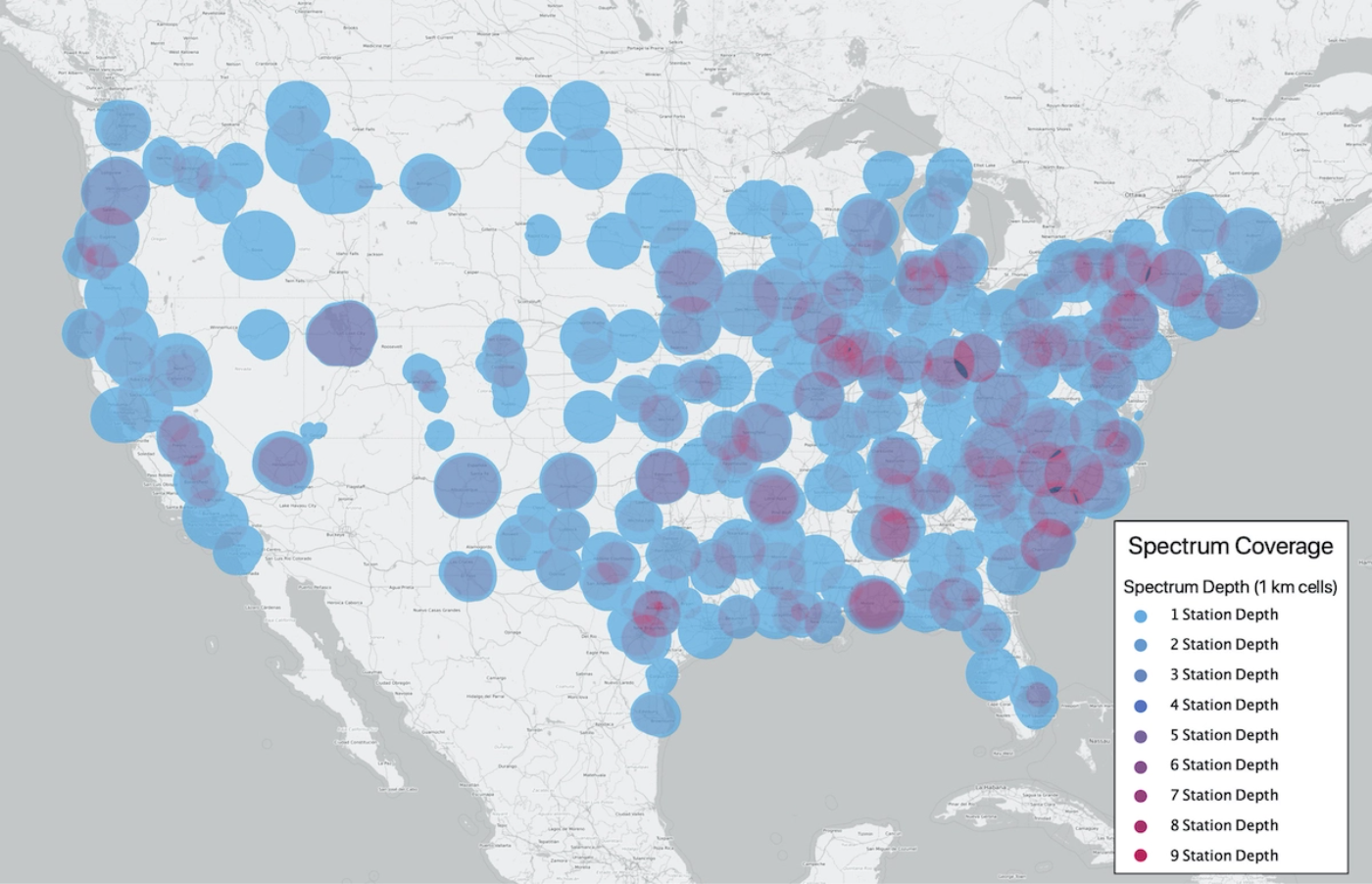
Coverage
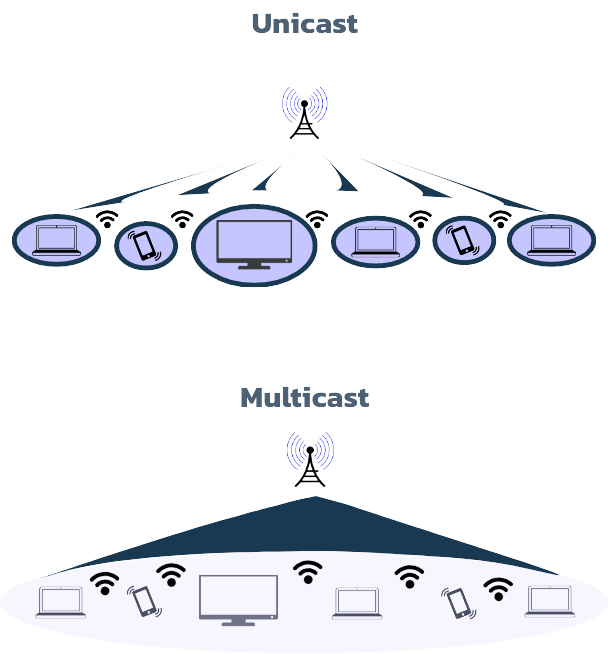
Unicast vs. Multicast
One-To-Many
Multicast distribution is a key example of wholesale as a service or distribution as a service in action. Multicast distribution uses the capabilities enabled by ATSC 3.0 to automate datacasting in a one-to-many format, or multicasting, to IoT and other edge devices.
Through PEAK3, multicast can be enabled on the edge. Architecture that incorporates ATSC 3.0 with new cloud, SD-WAN, and orchestration technologies allows enterprise companies to rent spectrum dynamically and when needed.
Largescale software updates for “edge-heavy” industry (like Building/Industrial Automation, Automotive, and Critical Infrastructure) are clear examples of multicasting at work. Electric and autonomous vehicles require the continuous ability to update software for new functionality, bug fixes, and navigation. For autonomous vehicles in particular, safety is at stake, and car manufacturers must update software within hours—not days or months. Once hundreds of thousands of vehicles requiring software updates are on the road, broadcasting a multi-gigabit software update over a unicast network will cause network bottlenecks as periods of accommodation for terabits of traffic will be needed. As an alternative, PEAK3’s ATSC 3.0 broadcasting service enabled by multicasting will make it possible to simultaneously deliver software updates to infinite numbers of IoT devices such as smart vehicles.